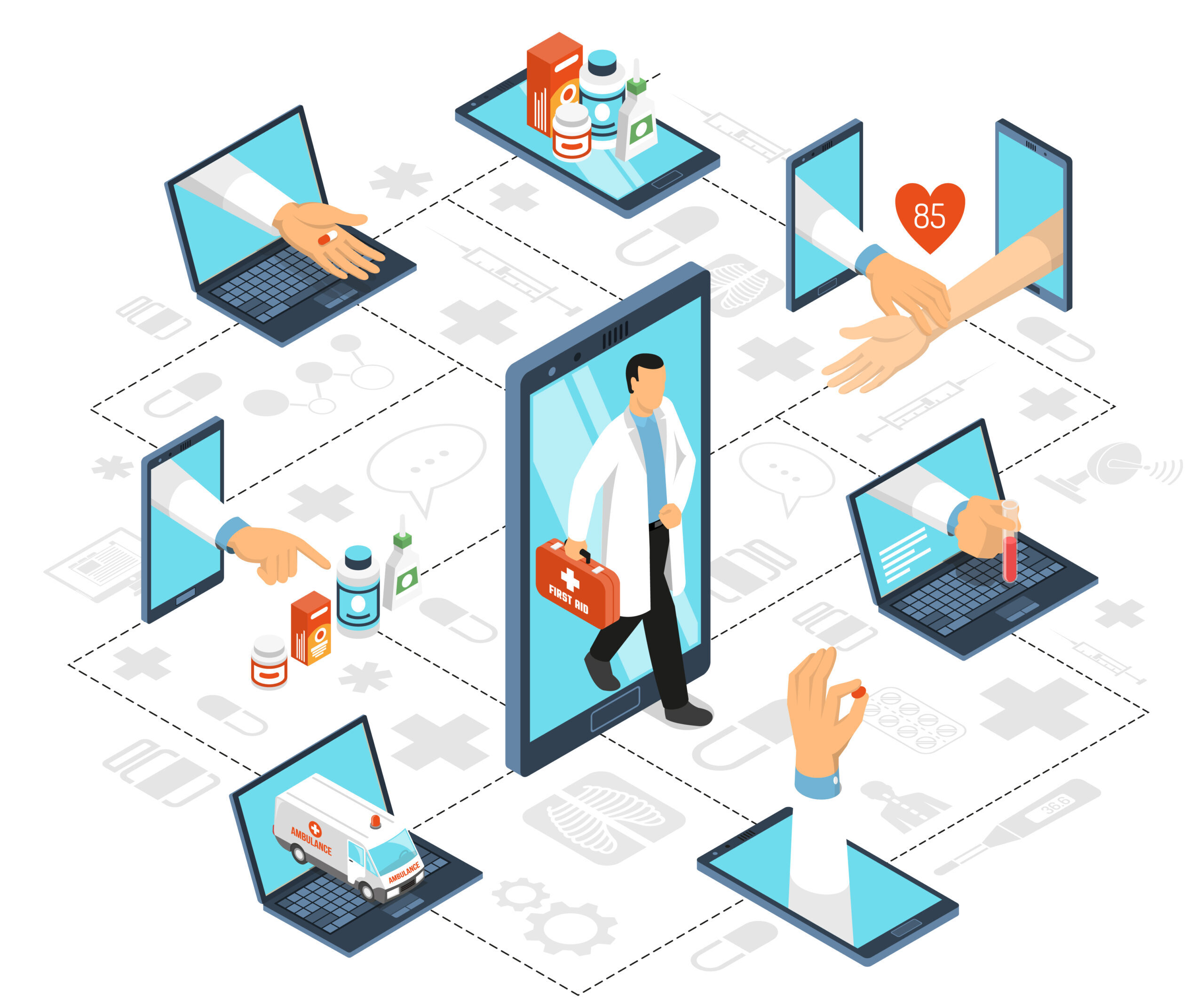
Health for life: Discover the balance of life
In our busy lives, we often forget about our health because we have so much to do. But having good health is like having a strong foundation for a happy life. “Health for Life” isn’t something temporary; it’s about taking care of yourself for a long, happy life. This article will show you some easy ways to do that.
Eat Good Food
Eating healthy food is really important. You should eat fruits, vegetables, lean meats, whole grains, and good fats. Try not to eat too much processed or sugary food. Your body needs these healthy foods to work well.
Move Your Body
Exercising is not just about losing weight. It’s about making your body strong and flexible. You can do this by walking, playing sports, or praying. Maintain and do these regularly.
Get Enough Sleep
Sleeping is when your body fixes itself. You should get 7-8 hours of sleep at night. It will help you feel better and think more creatively.
Deal with Stress
Stress can make you sick, so it’s important to manage it. You can do this by doing relaxing things like deep breathing or yoga. It’s also good to talk to someone when you’re feeling stressed.
Go to the Doctor
Seeing a doctor for regular check-ups is a good idea. They can catch problems early and help you stay healthy. Don’t forget to get vaccines and tests as your doctor recommends.
Take Care of Your Mind and Feelings
Health isn’t just about your body; it’s about your mind and feelings too. Try to relax and do things you enjoy. Talk to friends and family when you’re feeling down, and it’s okay to ask for help when you need it.
Avoid Bad Habits
Smoking, drinking alcohol, and using drugs are harmful to your health. If you have these habits, you should leave these. Your body can heal when you stop these bad habits.
Health for life: Role of a dispensary
Dispensaries help people with their health in the “Health for Life” program. They provide important medical treatments and information.
- Medicines: Dispensaries offer medicines like medical cannabis to help with pain and other health issues.
- Advice: The people working at dispensaries can give advice and share knowledge about different products, so you can make good choices for your health.
- Safety: Dispensaries make sure that the products they provide are safe and regulated, which means they meet quality standards.
- Learning: Some dispensaries offer classes and resources to teach people how to use medicines for better health.
In simple words, dispensaries in “Health for Life” help people by giving them the right medicines, advice, and information to stay healthy.
Let’s discuss about Health service of different places:
Health for Life in White Marsh
The health system in White Marsh, a suburban area in Baltimore. Key features of the health system in White Marsh include:
Healthcare Facilities: White Marsh is home to a range of healthcare facilities, including hospitals, clinics, and medical practices, offering comprehensive care to residents.
Access to Specialized Care: Residents have access to specialized medical care, including services related to cardiology, orthopedics, pediatrics, and more.
Primary Care: Primary care providers in the area offer essential healthcare services, such as routine check-ups, preventive care, and basic medical treatments.
Community Health Initiatives: White Marsh promotes community health through initiatives like health fairs, wellness programs, and educational campaigns to encourage healthy lifestyle choices.
Collaboration: Healthcare providers in White Marsh often collaborate with schools, businesses, and community organizations to address local health needs and ensure residents have the resources they need to maintain good health.
Proximity to Baltimore: The proximity of White Marsh to Baltimore allows residents to access world-class medical facilities and specialists in the city for more complex or specialized healthcare needs.
Health for Life in Ellsworth
Ellsworth, a small city located in Maine, has a well-organized healthcare system that caters to the needs of its residents. Key features of the health system in Ellsworth include:
Hospitals and Medical Facilities: Ellsworth is home to several hospitals, clinics, and medical facilities that provide a wide range of healthcare services. The Maine Coast Memorial Hospital is a prominent healthcare provider in the area.
Primary Care: Residents have access to primary care physicians who offer general healthcare services, routine check-ups, and preventive care. This ensures that individuals can easily manage their health and well-being.
Specialized Services: Ellsworth’s healthcare system offers specialized services, including access to specialists such as cardiologists, orthopedists, and other medical experts. This ensures that residents can receive specialized care without the need to travel long distances.
Community Health Initiatives: The city promotes community health through various initiatives, including health fairs, wellness programs, and educational campaigns. These efforts encourage healthy lifestyles and preventive care.
Telehealth: Like many healthcare systems, Ellsworth has embraced telehealth services, making it easier for residents to consult with healthcare professionals remotely, especially in cases where in-person visits are not necessary.
Health Insurance Access: Various health insurance options are available to residents, ensuring that healthcare services are financially accessible to a broad range of the population.
Health for Life in Baltimore
The health system in Baltimore is characterized by a diverse and robust healthcare infrastructure. Key features include:
World-Class Medical Institutions: Baltimore is home to prestigious medical institutions such as Johns Hopkins Hospital, University of Maryland Medical Center, and MedStar Health facilities. These hospitals are at the forefront of medical research and provide high-quality care.
Research and Innovation: The city is a hub for medical research and innovation, with a strong emphasis on cutting-edge treatments, clinical trials, and healthcare technology.
Public Health Initiatives: Baltimore’s health department is actively involved in public health initiatives, disease prevention, and health promotion. Programs target issues like vaccination, maternal and child health, and substance abuse treatment.
Community Health Centers: The city offers accessible care through a network of community health centers, ensuring that underserved populations have access to primary care and preventive services.
Addressing Health Disparities: Baltimore is committed to addressing health disparities, particularly in underserved neighborhoods, by providing resources and services to bridge the gap in healthcare access.
Medical Education: The city is a center for medical education, training healthcare professionals and contributing to the workforce of the future.
Health for Life in Cave Creek
Cave Creek, a town in Arizona, has a healthcare system that primarily serves its residents through a combination of local healthcare providers, clinics, and medical facilities. While Cave Creek itself is a relatively small town, it is part of the larger Phoenix metropolitan area, which means residents have access to a broader network of medical services.
The healthcare system in Cave Creek includes:
Local Clinics: Cave Creek has several primary care clinics and specialty practices, offering services such as general medical care, pediatrics, and more. These clinics are often the first point of contact for residents seeking medical attention.
Hospitals: While Cave Creek doesn’t have its own hospitals, there are numerous hospitals and medical centers in the Phoenix metropolitan area, providing a wide range of specialized medical services. Residents can access emergency care, surgeries, and advanced medical treatments within a reasonable distance.
Specialty Care: Residents can also access specialized healthcare services in nearby cities, including Scottsdale and Phoenix, which are known for their medical expertise in areas such as cardiology, oncology, and neurology.
Telemedicine: Telemedicine services have become increasingly popular, allowing residents to consult with healthcare providers remotely, which can be especially beneficial in rural areas like Cave Creek.
Health Education: Community organizations and health departments in the region may offer health education programs and resources to promote wellness and preventive care.
The healthcare system in Cave Creek benefits from its proximity to the broader healthcare resources in the Phoenix metropolitan area, ensuring that residents have access to a wide range of medical services and specialty care.
Health for Life in Bethesda
Health in Bethesda, Maryland, has a rich history and continues to play a vital role in the community. Bethesda is well-known for its contributions to healthcare and medical research. Here’s a brief overview of health in Bethesda and its history:
- Medical Research Hub: Bethesda is known for the National Institutes of Health (NIH), a major medical research center that makes important discoveries in health and medicine.
- Walter Reed National Military Medical Center: This hospital has cared for military personnel for many years and continues to do so.
- Education and Healthcare: Bethesda has institutions like the Uniformed Services University of the Health Sciences (USUHS), which trains medical professionals for the military.
- Community Health Services: The area has hospitals, clinics, and wellness programs to ensure people can get good healthcare.
- Healthcare and Research Advancements: Bethesda’s healthcare institutions have helped improve medical knowledge, treatments, and clinical trials that help people not just in the community but around the world.
Health for Life in highlands

The health system in Highlands is characterized by a focus on holistic well-being and access to healthcare services that cater to the needs of the local population. It typically includes:
Community Health Initiatives: Highlands often emphasizes community health programs, promoting outdoor activities, and wellness events to encourage healthy lifestyles.
Primary and Specialty Care: Residents have access to primary care providers and specialized medical services to address a wide range of healthcare needs.
Health Education: Public health campaigns and educational resources are commonly employed to raise awareness about preventive care and health promotion.
Natural Health Benefits: The region’s natural beauty and surroundings play a role in promoting health, encouraging residents to engage in outdoor activities and appreciate the positive impact of nature on well-being.
Holistic Wellness: Holistic approaches to health and wellness, including complementary and alternative medicine, may be integrated into the healthcare system.
The specific healthcare facilities and services in Highlands can vary, but the community’s focus on well-rounded health and access to necessary care contribute to a comprehensive health system that supports the residents’ well-being.
At the end
“Health for Life” is a journey that lasts a long time. By eating well, moving your body, sleeping enough, managing stress, going to the doctor, taking care of your mind and feelings, and avoiding bad habits, you can stay healthy for a happy life. Your health is very important, so take care of it today, and it will make your life better in the future.
References:
-
Local Government and Community Websites: Official websites of White Marsh, Ellsworth, Baltimore, Cava Creek, Bethesda, and Highlands for information on their healthcare and community health programs.
-
Healthcare Providers: Local healthcare providers, hospitals, and clinics in each region for statistics, services, and community outreach programs.
-
Health Department Reports: Reports and publications from county or city health departments in the respective regions. These reports often contain valuable health-related data and initiatives.
-
Community Health Organizations: Organizations such as non-profits or community health centers may provide information on their work in promoting health and wellness.
-
Academic Research: Academic institutions in the regions may have conducted research related to healthcare, community health, or public health initiatives. Their publications and studies.
-
News Articles: Local newspapers and news outlets that covered community health programs, healthcare access, and initiatives in their coverage area.
Image credit: Image by Freepik, www.freepik.com/free-photo/beautiful-woman-listening-music-stretching_5938816. , Image by wayhomestudio on Freepik, Image by cookie_studio on Freepik, Image by upklyak on Freepik, Image by DCStudio on Freepik, Image by KamranAydinov on Freepik
Writer is the graduate health technologist from University of Dhaka and former paramedic of Urban primary health care project, Dhaka.